While Tattooing has existed in the European peninsula since Neolithic times, the art form saw a gradual decline during the spread of Christianity throughout the continent.
Associated with paganism and barbarianism, tattooing was suppressed, leading it to be almost forgotten about due to stigmatization.
Having been forgotten about and stigmatized for so long, just how did tattooing make a resurgence back into Europe becoming one the most popular and accepted art forms today? Let’s find out.
Featured image credit: winonapost.com
Sailors And The Resurgence Of Tattooing
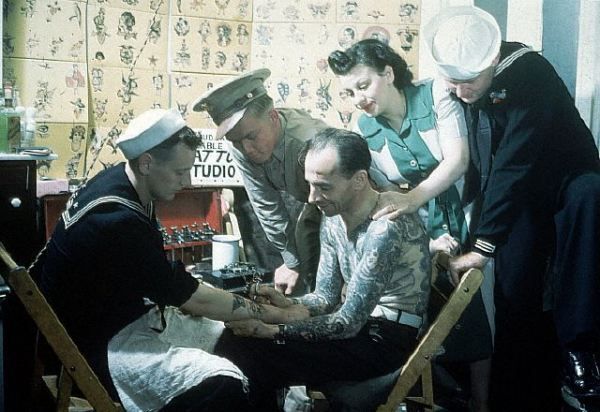
The resurgence of tattooing can be mostly attributed to sailors in the 16th to 18th centuries.
When European sailors traveled across the world’s oceans, they encountered many cultures where tattooing was prevalent, such as in Polynesia and the Pacific Islands.

Photo credit: Military.com
Fascinated by these encounters, sailors chose to get their own tattoos from these tribes as mementos of their journeys that they could bring home.
Captain James Cook, in particular, played a significant role in the history of tattooing in the Western world and is credited with reintroducing the concept of tattooing to Europe.
Captain James Cook
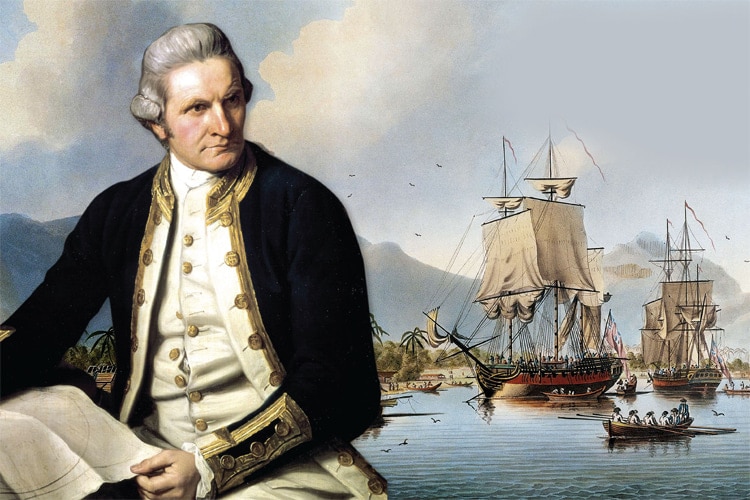

Photo credit: SurferToday.com
Captain James Cook partook in three voyages to the Pacific from 1768 to 1779.
During these voyages, he and his crew encountered various Polynesian cultures where tattooing was a highly developed and integral part of social and cultural life.
During a trip to Tahiti, Captain James recorded in his expedition logs the Tahitian word "tatau," which would evolve to become the word ‘Tattoo’ that we all know today.
The encounters fascinated Cook's crew so much that many of them including officers and naturalists, returned to Europe with tattoos, making them walking testimonials to the rich cultural practices they had witnessed.
This sparked interest among Europeans, who were intrigued by these exotic markings and the stories behind them.
Once the crew had returned to England, their accounts were published alongside descriptions and illustrations of their adventures, fueling interest in tattooing.
Tattoos became seen as a symbol of adventure, exoticism, and cultural exploration, helping to shift the European perceptions of tattooing from a practice seen as primitive or barbaric to one of artistic and cultural significance.
Post James Cook
After James Cook's adventures brought Tattooing back into the European zeitgeist, tattooing still remained largely associated with sailors, soldiers, and adventurers who got them as souvenirs from their travels to exotic destinations.
However, during the 19th century tattooing began to gain popularity among the European aristocracy.
This is thanks partly to King Edward VII of the United Kingdom, who got a tattoo of a Jerusalem Cross during his visit to the Holy Land with members of the aristocracy following suit, viewing tattoos as exotic luxuries that demonstrated wealth and worldliness.
This period saw the rise of professional tattoo artists who began to set up shops in major European cities.
Source: pinterest.ph
In 1891, an American inventor named Samuel O’Reilly invented the first tattoo machine, revolutionizing the tattoing scene by making it quicker, easier, and less painful to get a tattoo.
His technology quickly spread to Europe, enabling more intricate and detailed designs and reducing the exclusivity of tattoos by making them accessible to wider populations.
After World War II, tattooing entered a new phase with increased globalization.
As American and European cultures mixed, the soldiers returning from overseas brought back new tattoo styles and techniques learned from each other.
This era also saw the beginning of tattoo conventions, which played a significant role in spreading tattoo culture.
In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, tattooing became increasingly accepted and mainstream in Europe, part of a global trend toward body art.
It is now seen as a form of personal and artistic expression across all levels of society.
The stigma once associated with tattoos has diminished, and the art form continues to evolve with influences from around the world, including the resurgence of traditional and tribal tattooing techniques.
Today, Europe hosts some of the world’s most famous tattoo conventions and is home to numerous renowned artists.
The diversity of styles and the quality of artistry available make it a rich field for those interested in tattoos, either as personal expression or as art.
Conclusion
It’s clear that the sailors of yesteryear were not just explorers of new lands but also pioneers of cultural exchange.
Their tattooed bodies showcased their encounters with distant cultures, sparking a renaissance in tattoo art that continues to thrive today throughout Europe and even the wider world.
If you’re interested in learning more tattooing history, you can learn about about the American tattooing icon Sailor Jerry Collins, or you can learn more about ancient tattooing methods or if you love sailor tattoos, check out one of the stereotypical Sailor Tattoos with these Anchor Tattoo Designs.
- Kristen Bell Tattoos - July 15, 2024
- Risks of Tattooing - July 3, 2024
- Early Tattooing Methods - June 22, 2024

